Business inventory barcode systems are transforming the way businesses manage their inventory, offering a seamless and efficient solution for tracking and optimizing stock levels. This technology empowers businesses to streamline operations, reduce errors, and gain real-time visibility into their inventory.
From retail stores to manufacturing facilities, barcode systems are proving invaluable in enhancing inventory accuracy, minimizing waste, and improving overall supply chain management.
Business Inventory Barcode System Overview
A business inventory barcode system is an electronic system that uses barcodes to track inventory items. Barcodes are unique identifiers that are printed on product labels. When a barcode is scanned, it can be used to identify the product and track its movement through the supply chain.
There are many benefits to implementing a barcode system for inventory management. These benefits include:
Improved Accuracy
Barcodes can help to improve the accuracy of inventory records. When items are scanned, the barcode reader can automatically identify the product and update the inventory record. This eliminates the need for manual data entry, which can lead to errors.
Increased Efficiency
Barcodes can help to increase the efficiency of inventory management tasks. For example, barcodes can be used to speed up the process of receiving, shipping, and counting inventory.
Reduced Costs
Barcodes can help to reduce the costs of inventory management. By improving accuracy and efficiency, barcodes can help businesses to reduce the amount of time and money spent on inventory management tasks.
Types of Barcode Systems
Barcode systems employ various symbologies, each with unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these differences helps businesses choose the most appropriate barcode type for their inventory management needs.
Linear Barcodes
Linear barcodes are one-dimensional, consisting of parallel lines of varying widths and spaces. They are widely used due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Common linear barcode symbologies include:
- UPC (Universal Product Code):Used for retail products, UPC barcodes contain 12 digits encoding product information and manufacturer details.
- EAN (European Article Number):Similar to UPC, EAN barcodes have 13 digits and are commonly found on products in Europe and other regions.
- Code 39:A versatile barcode that can encode both numbers and letters, making it suitable for industrial and healthcare applications.
2D Barcodes, Business inventory barcode system
2D barcodes are two-dimensional, storing data in both the horizontal and vertical directions. They offer higher data capacity and can encode more complex information compared to linear barcodes. Popular 2D barcode symbologies include:
- QR Code (Quick Response Code):Widely used in marketing and advertising, QR codes can store text, URLs, and other data and can be easily scanned by smartphones.
- Data Matrix:A high-density 2D barcode suitable for small items or where space is limited.
- PDF417:A high-capacity 2D barcode designed for applications requiring large amounts of data, such as inventory tracking and shipping labels.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Each barcode symbology has its advantages and disadvantages:
| Symbology | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Barcodes | Simple and cost-effectiveEasy to scan and decode | Limited data capacitySusceptible to damage |
| 2D Barcodes | High data capacityCan encode complex information | More complex to scan and decodeMay require specialized equipment |
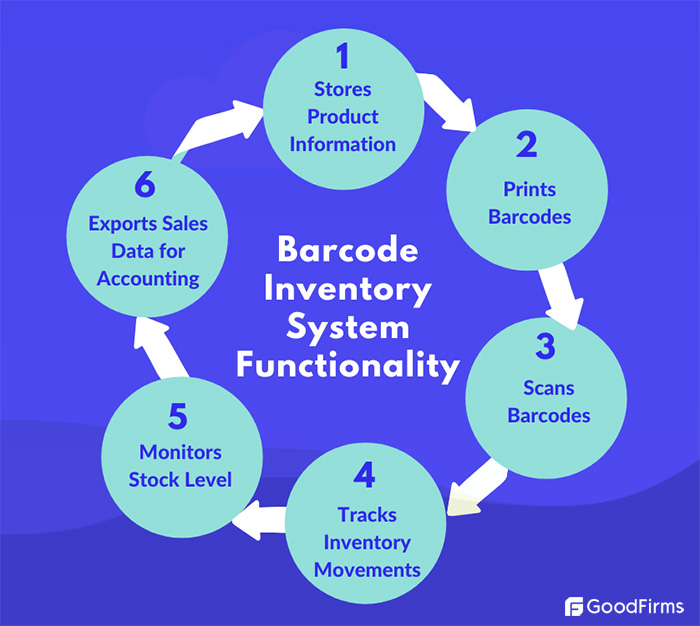
Hardware and Software Components: Business Inventory Barcode System
A barcode system relies on a combination of hardware and software components to effectively manage inventory. These components work together to capture, decode, and manage inventory data, enabling businesses to streamline their inventory processes and enhance accuracy.
Barcode Scanners
- Barcode scanners are essential hardware devices used to capture and decode barcode data. They come in various forms, including handheld, stationary, and wearable options.
- Handheld scanners are portable and allow for easy scanning of items in different locations.
- Stationary scanners are fixed in place and are ideal for high-volume scanning applications, such as in warehouses or retail checkout counters.
- Wearable scanners provide hands-free scanning, increasing efficiency in environments where mobility is crucial.
Barcode Printers
- Barcode printers are used to create barcode labels that can be attached to inventory items. These printers can generate high-quality barcodes that are durable and resistant to wear and tear.
- There are various types of barcode printers available, including thermal transfer, direct thermal, and laser printers.
- The choice of printer depends on the specific requirements of the business, such as the volume of labels needed, the durability required, and the cost.
Barcode Software
- Barcode software is a crucial component of a barcode system, as it manages and processes the data captured by barcode scanners.
- This software can be integrated with other business systems, such as inventory management systems or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
- Barcode software allows businesses to track inventory levels, manage stock movements, and generate reports for analysis and decision-making.
Ending Remarks
As businesses continue to adopt barcode systems, the future holds even greater advancements. Integration with emerging technologies like RFID and IoT promises to further enhance inventory management capabilities, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions and optimize their operations like never before.
Clarifying Questions
What are the key benefits of implementing a barcode system for inventory management?
Barcode systems offer numerous benefits, including improved inventory accuracy, reduced labor costs, enhanced efficiency, and real-time visibility into stock levels.
What types of barcode systems are available?
There are various barcode symbologies available, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Common types include Code 39, Code 128, and QR codes.
What hardware and software components are needed for a barcode system?
Essential hardware components include barcode scanners and printers. Barcode software plays a crucial role in managing and interpreting inventory data.
How can businesses ensure successful implementation of a barcode system?
Successful implementation requires careful planning, training, and integration with existing business systems. Regular maintenance and updates are also essential.