Navigating the complexities of inventory management can be a daunting task, but with the right tools and strategies, you can streamline your operations and optimize your stock levels. Enter the business inventory checklist, your comprehensive guide to ensuring accurate tracking, efficient verification, and informed decision-making.
Delve into the intricacies of inventory management systems, physical verification techniques, optimization strategies, control methods, and reporting analysis. Empower yourself with the knowledge and tools to maintain optimal inventory levels, minimize costs, and drive your business towards success.
Inventory Management System
An inventory management system is a crucial tool for businesses to accurately track and manage their inventory levels. It helps businesses optimize their inventory levels, reduce costs, and improve customer service.An effective inventory management system should include the following key features and functionalities:* Real-time inventory tracking
- Automated inventory replenishment
- Inventory forecasting
- Reporting and analytics
There are many different inventory management software solutions available, each with its own unique capabilities. Some of the most popular inventory management software solutions include:* SAP ERP
- Oracle NetSuite
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
- QuickBooks Enterprise
- Fishbowl Inventory
The choice of inventory management software will depend on the specific needs of the business.
Physical Inventory Verification
Physical inventory verification is the process of comparing the physical count of inventory items to the records in the inventory management system. This process is essential for ensuring that the inventory records are accurate and that the business has a clear understanding of its inventory levels.
Regular Inventory Counts
Regular inventory counts are an important part of physical inventory verification. These counts should be conducted on a regular basis, such as monthly or quarterly, to ensure that the inventory records are up-to-date. Regular inventory counts can help to identify any discrepancies between the physical count and the inventory records, which can then be investigated and corrected.
Cycle Counting
Cycle counting is a more frequent form of inventory verification that involves counting a small portion of the inventory on a regular basis. Cycle counting can help to identify any discrepancies between the physical count and the inventory records more quickly than regular inventory counts.
This can help to prevent any major discrepancies from occurring and can also help to improve the accuracy of the inventory records.
Tips for Ensuring Accuracy
There are a number of tips that businesses can follow to ensure the accuracy of their physical inventory verification process. These tips include:
- Using a barcode scanner to capture the inventory counts.
- Training staff on the proper procedures for conducting physical inventory counts.
- Verifying the accuracy of the inventory counts by having a second person count the same items.
- Reconciling the physical inventory counts to the inventory records in the inventory management system.
- Investigating and correcting any discrepancies between the physical inventory counts and the inventory records.
Inventory Optimization
Inventory optimization is the process of determining the optimal level of inventory to hold, considering factors such as demand, lead time, and holding costs. The goal of inventory optimization is to minimize total inventory costs while maintaining an acceptable level of customer service.
There are a number of different inventory optimization techniques that can be used, including:
- ABC analysis: ABC analysis is a technique that classifies inventory items into three categories based on their annual dollar usage. Class A items are the most valuable items and should be managed closely to minimize inventory costs. Class B items are moderately valuable and should be managed with a balance of cost and service.
Class C items are the least valuable items and can be managed with a focus on minimizing holding costs.
- Safety stock calculations: Safety stock is the amount of inventory that is held above the expected demand to protect against unexpected fluctuations in demand or lead time. Safety stock calculations can be used to determine the optimal level of safety stock to hold for each inventory item.
Inventory optimization can have a significant impact on a company’s efficiency and costs. By optimizing inventory levels, companies can reduce holding costs, improve customer service, and free up cash flow that can be used for other purposes.
For example, a company that sells electronics products was able to reduce its inventory costs by 15% by implementing an inventory optimization program. The company used ABC analysis to classify its inventory items and safety stock calculations to determine the optimal level of safety stock to hold for each item.
By optimizing its inventory levels, the company was able to free up cash flow that it used to invest in new product development.
Inventory Control Methods
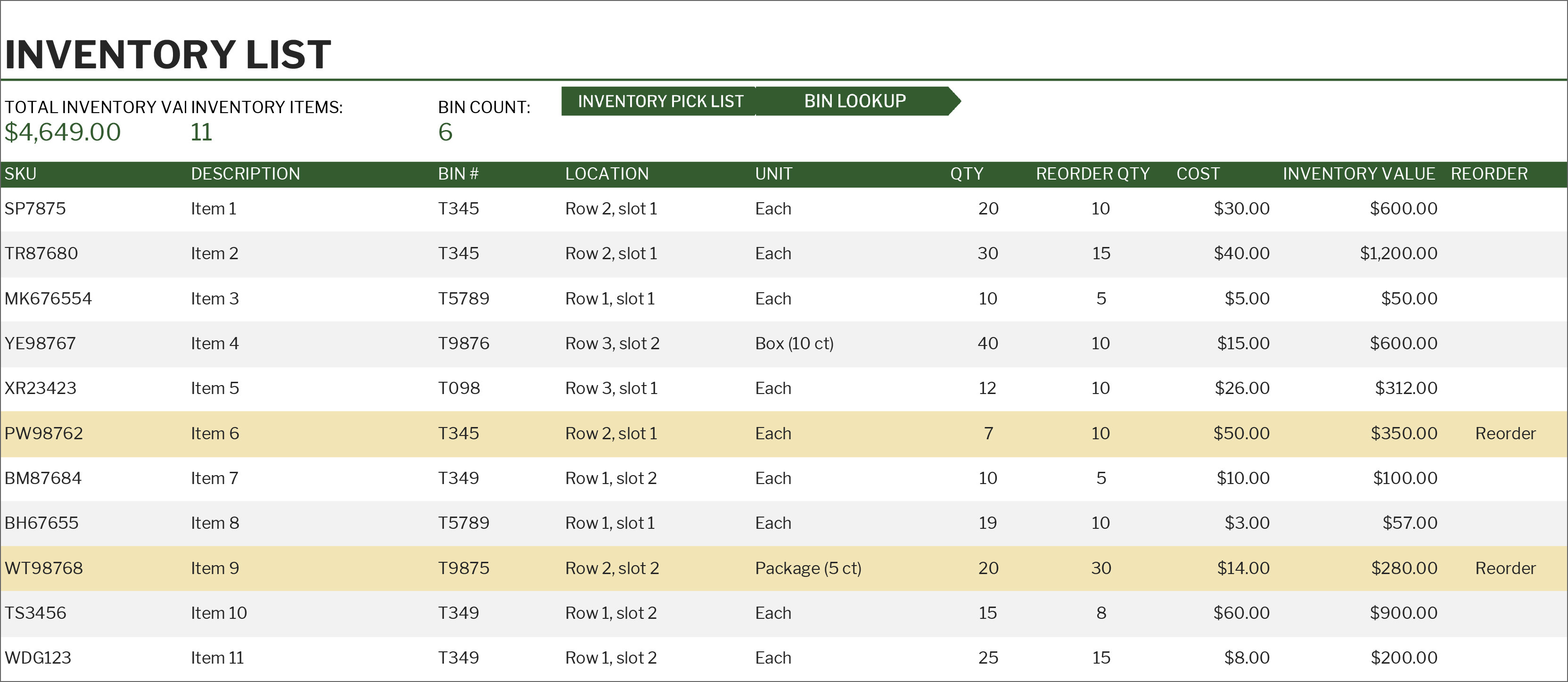
Inventory control methods are techniques used to manage and track inventory levels effectively. They help businesses optimize stock levels, reduce waste, and improve overall inventory management.
FIFO (First-In, First-Out), Business inventory checklist
- Assumes that the oldest inventory is sold first.
- Advantages:
- Matches the physical flow of inventory.
- Prevents obsolete inventory from being held.
- Disadvantages:
- Can result in higher cost of goods sold (COGS) during periods of inflation.
- May not accurately reflect the current value of inventory.
LIFO (Last-In, First-Out)
- Assumes that the newest inventory is sold first.
- Advantages:
- Can result in lower COGS during periods of inflation.
- May more accurately reflect the current value of inventory.
- Disadvantages:
- Can lead to obsolete inventory being held.
- May not match the physical flow of inventory.
Weighted Average
- Calculates the average cost of inventory based on all purchases.
- Advantages:
- Provides a more stable COGS.
- Easier to calculate than FIFO or LIFO.
- Disadvantages:
- May not accurately reflect the current value of inventory.
- Can result in a mismatch between physical and accounting inventory.
Selecting the Appropriate Method
The choice of inventory control method depends on several factors, including:
- Nature of the business
- Industry practices
- Tax implications
- Desired level of accuracy
For businesses with high inventory turnover and a consistent flow of goods, FIFO or weighted average may be suitable. For businesses with slow inventory turnover and a risk of obsolete inventory, LIFO may be more appropriate.
Inventory Reporting and Analysis
Inventory reporting and analysis play a crucial role in efficient inventory management. Regular reporting provides visibility into inventory levels, movement, and performance, enabling businesses to make informed decisions.
Types of Inventory Reports
Various types of inventory reports exist, each serving a specific purpose:
- Inventory Valuation Report:Summarizes the value of inventory on hand, classified by categories or locations.
- Stock Status Report:Provides real-time information on inventory levels, highlighting items that are running low or overstocked.
- Inventory Turnover Report:Calculates the rate at which inventory is sold and replaced, indicating inventory efficiency.
- ABC Analysis Report:Classifies inventory items based on their value and usage, helping businesses prioritize inventory management efforts.
Benefits of Inventory Analysis
Inventory analysis involves examining historical and current inventory data to identify trends and patterns. It helps businesses:
- Forecast Demand:By analyzing historical sales data, businesses can predict future demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
- Identify Slow-Moving Items:Analysis reveals items that are not selling well, allowing businesses to reduce inventory carrying costs.
- Optimize Safety Stock:Analysis determines the appropriate safety stock levels to prevent stockouts while minimizing excess inventory.
- Improve Inventory Turnover:By analyzing inventory turnover rates, businesses can identify areas for improvement and increase inventory efficiency.
Ultimate Conclusion: Business Inventory Checklist
Mastering inventory management is crucial for businesses of all sizes. By implementing the principles Artikeld in this checklist, you can gain complete control over your stock, reduce waste, and maximize profitability. Remember, an organized and well-managed inventory is the backbone of efficient operations and customer satisfaction.
FAQ Overview
What are the key features of an effective inventory management system?
Real-time tracking, automated inventory updates, customizable reports, and integration with other business systems.
How often should I conduct physical inventory verification?
Regularly, depending on the size and nature of your business. Consider monthly or quarterly counts, supplemented by cycle counting.
What are the benefits of inventory optimization?
Reduced storage costs, improved cash flow, increased customer satisfaction, and better decision-making.