Inventory systems for businesses play a pivotal role in streamlining operations, minimizing costs, and maximizing profitability. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of inventory management, providing valuable insights and practical strategies to help businesses optimize their stock levels.
From understanding the fundamentals of inventory systems to implementing cutting-edge technologies, this guide covers everything you need to know to effectively manage your inventory and drive business success.
Inventory Systems Overview
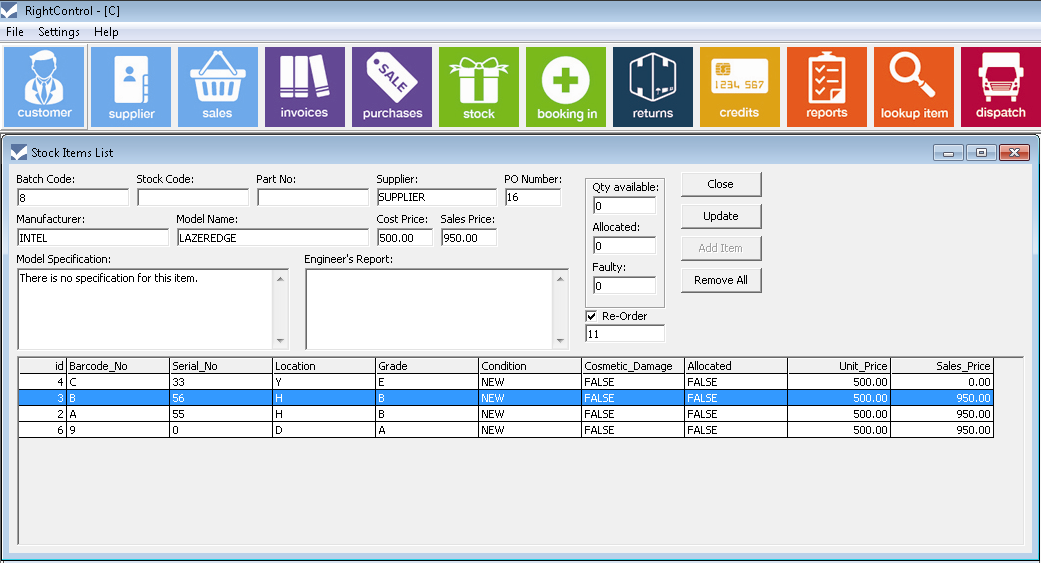
Inventory systems are an integral part of business operations, enabling businesses to effectively manage their stock levels and meet customer demand. They provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing businesses to optimize their supply chain, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Various types of inventory systems are used in different industries, each tailored to specific business requirements. These include:
Perpetual Inventory Systems
Perpetual inventory systems continuously update inventory records as transactions occur. This real-time tracking provides businesses with accurate and up-to-date information on stock levels, allowing for efficient inventory management and timely replenishment.
Periodic Inventory Systems
Periodic inventory systems update inventory records at specific intervals, typically at the end of a period or when a physical count is performed. This system is less labor-intensive than perpetual inventory systems but may result in less accurate inventory data.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory Systems
JIT inventory systems aim to minimize inventory levels by receiving inventory only when needed for production or sale. This approach reduces holding costs and improves inventory turnover but requires close coordination with suppliers and efficient logistics.
Benefits of Inventory Systems
- Improved inventory accuracy and visibility
- Reduced inventory costs
- Enhanced customer satisfaction
- Optimized supply chain management
Challenges of Implementing Inventory Systems
- Cost of implementation and maintenance
- Complexity of integrating with other systems
- Data accuracy and integrity
- Training and adoption by employees
Inventory Management Strategies
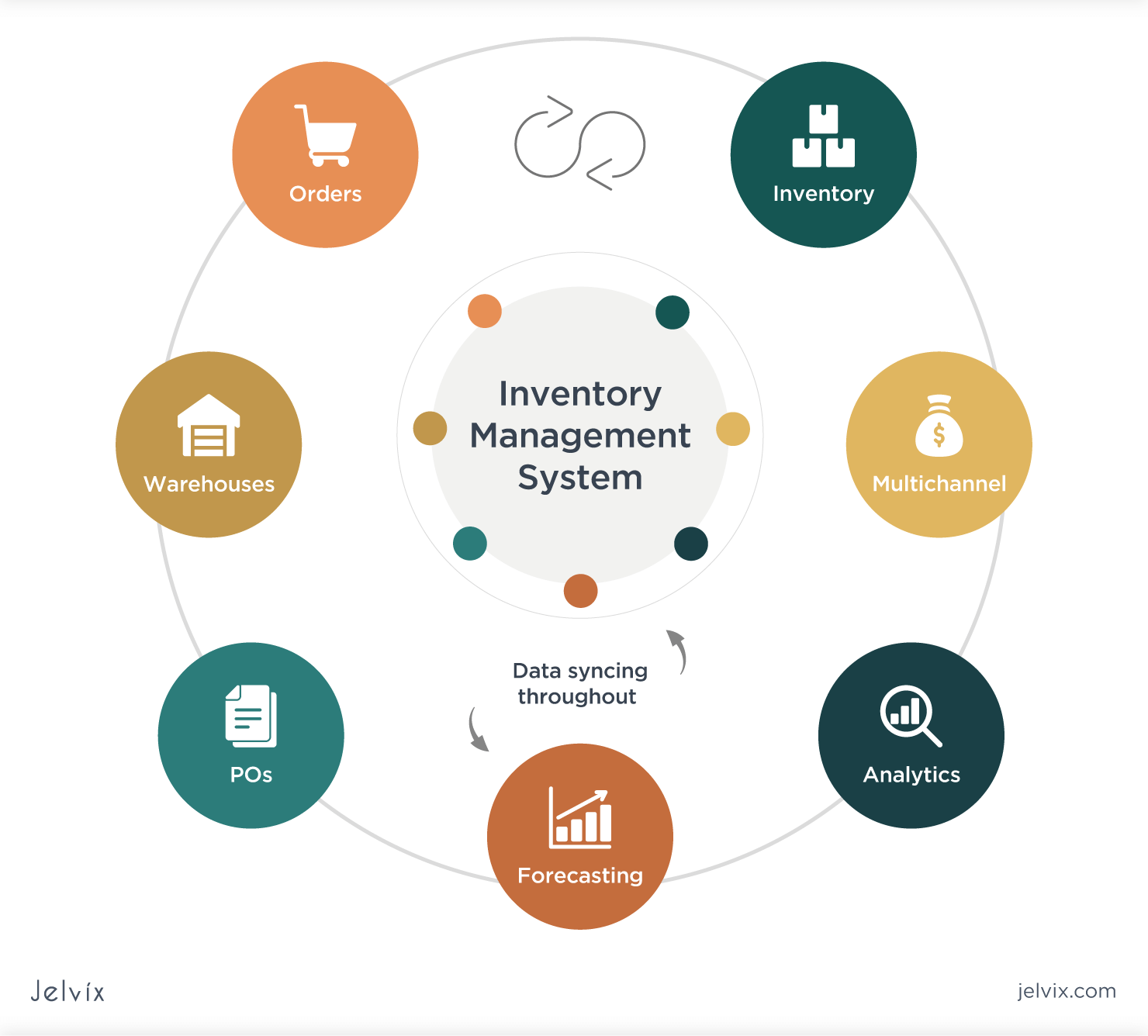
Effective inventory management involves adopting strategies that optimize stock levels while minimizing costs. Two widely used strategies are just-in-time (JIT) and vendor-managed inventory (VMI).
Just-in-Time (JIT)
JIT aims to maintain minimal inventory levels by receiving goods only when needed for production or sales. This approach reduces holding costs and improves inventory turnover. Key advantages include reduced waste, increased efficiency, and improved cash flow.
Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
VMI involves outsourcing inventory management to the supplier. The supplier monitors inventory levels and replenishes stock as needed. This strategy benefits businesses by reducing inventory costs, improving supplier relationships, and freeing up internal resources.
Comparison of JIT and VMI
- Inventory Levels: JIT maintains low inventory levels, while VMI allows for higher inventory levels.
- Cost: JIT reduces holding costs, while VMI may increase supplier costs.
- Control: JIT gives the business more control over inventory, while VMI gives the supplier more control.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Inventory Management
To measure the effectiveness of inventory management, several KPIs can be used:
- Inventory Turnover: Measures how quickly inventory is sold and replaced.
- Days Sales of Inventory (DSI): Indicates the average number of days it takes to sell inventory.
- Inventory Accuracy: Assesses the accuracy of inventory records compared to physical stock.
- Fill Rate: Measures the percentage of customer orders that are fulfilled from available inventory.
Inventory Optimization Techniques
Optimizing inventory levels is crucial for businesses to minimize costs and maximize efficiency. Various techniques can be employed to achieve this, including ABC analysis, safety stock management, and data analysis.
ABC Analysis
ABC analysis classifies inventory items into three categories based on their value and usage:
- A-items: High-value items that account for a significant portion of total inventory value.
- B-items: Moderate-value items that require closer monitoring.
- C-items: Low-value items that can be managed with less attention.
By identifying A-items, businesses can prioritize inventory management efforts and allocate resources accordingly.
Safety Stock Management
Safety stock refers to additional inventory held to buffer against unexpected demand fluctuations or supply chain disruptions.
Effective safety stock management involves determining optimal safety stock levels, which balance the cost of holding excess inventory with the risk of stockouts.
Data Analysis
Data analysis plays a vital role in inventory optimization. By analyzing historical demand patterns, businesses can identify trends, forecast future demand, and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
Additionally, data analysis can help identify slow-moving items, obsolete products, and other areas where inventory waste can be reduced.
Technology for Inventory Optimization
Technology has revolutionized inventory optimization. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and specialized inventory management software can automate inventory tracking, optimize replenishment schedules, and provide real-time data visibility.
Advanced technologies such as RFID and IoT can further enhance inventory accuracy and efficiency.
Inventory System Implementation
Implementing inventory systems can enhance business efficiency and profitability. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Assess Needs: Determine business requirements, inventory volume, and desired outcomes.
- Choose Software: Compare and select an inventory system software that aligns with business needs.
- Implement System: Train staff, configure software, and integrate with existing systems.
- Data Collection: Gather accurate and timely inventory data through barcodes, RFID, or manual entry.
- Process Optimization: Use inventory management techniques to optimize stock levels, minimize waste, and improve efficiency.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Track performance metrics, identify areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments.
Software Comparison Table
| Feature | Software A | Software B | Software C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inventory Tracking | Real-time visibility | Historical tracking | Multi-location tracking |
| Order Management | Integrated order processing | Third-party integrations | Advanced shipping options |
| Reporting and Analytics | Customizable reports | Predictive analytics | Mobile access |
| Cost | One-time purchase | Subscription-based | Pay-as-you-go |
Case Studies
Company A: Implemented an RFID-based inventory system, resulting in a 20% reduction in stock loss and a 15% increase in sales.
Company B: Used inventory optimization techniques to reduce inventory holding costs by 30% while maintaining optimal stock levels.
Company C: Integrated its inventory system with e-commerce platforms, leading to a 40% increase in online sales and improved customer satisfaction.
Inventory System Integration
Integrating inventory systems with other business systems is crucial for businesses to streamline operations and enhance efficiency. By connecting inventory systems with accounting and supply chain management systems, businesses can gain real-time visibility into inventory levels, automate processes, and improve decision-making.
Integration Process
- Establish Integration Objectives: Define the specific goals and benefits expected from the integration.
- Identify Integration Points: Determine the data and processes that need to be shared between the systems.
- Choose Integration Technology: Select the appropriate software or platform to facilitate data exchange.
- Implement Integration: Configure the systems and establish the necessary data flows.
- Test and Monitor: Thoroughly test the integration to ensure accuracy and troubleshoot any issues.
Benefits of Integration
- Improved inventory accuracy and reduced errors
- Automated inventory replenishment and purchase orders
- Real-time visibility into inventory levels across multiple locations
- Enhanced supply chain collaboration and reduced lead times
- Improved financial reporting and compliance
Challenges of Integration, Inventory systems for businesses
- Data compatibility and standardization issues
- Complexity of integrating multiple systems
- Cost and time required for implementation
- Security concerns and data protection
- Lack of technical expertise and resources
Future Trends in Inventory Systems

Inventory systems are undergoing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements. Artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology are emerging as key players, promising to reshape the way businesses manage their inventory.
AI-powered inventory systems can analyze vast amounts of data to predict demand, optimize stock levels, and automate inventory management tasks. This can lead to reduced costs, improved efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Blockchain Technology in Inventory Systems
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable nature, can enhance the transparency and security of inventory systems. It can provide a single, shared record of inventory transactions, eliminating the risk of data manipulation and fraud.
Final Review
In conclusion, inventory systems are essential for businesses of all sizes to optimize stock levels, reduce waste, and enhance operational efficiency. By embracing innovative technologies and adopting best practices, businesses can gain a competitive edge and achieve long-term success in today’s dynamic market landscape.
Commonly Asked Questions: Inventory Systems For Businesses
What are the benefits of implementing an inventory system?
Inventory systems provide numerous benefits, including improved accuracy, reduced costs, enhanced customer satisfaction, and better decision-making.
How can I choose the right inventory management strategy for my business?
The choice of inventory management strategy depends on factors such as industry, product type, and business goals. Common strategies include just-in-time (JIT), vendor-managed inventory (VMI), and periodic inventory.
What are some best practices for inventory optimization?
Best practices for inventory optimization include conducting regular inventory audits, implementing safety stock levels, and leveraging data analytics to identify and reduce waste.